Honors Geometry
Semester 2 Exam Study Guide
You are required to bring your own TI-84, and Chromebook fully charged. The test consists of 45 multiple choice questions.
Each question is worth 2 points. One point can be earned for showing the work that leads to your answer,
and the other point for choosing the correct choice.
The exam may be administered on your Chromebook at TestPortal.net, but
if there are technical difficulties, will be on paper.
If it is on TestPortals, the test will end if you attempt to leave the tab. There is one warning only, and if another attempt to leave the tab is attempted, the test will end early. To avoid this, activate "Do Not Disturb," close all apps on your Chromebook, and turn off all alarms and notifications.
Once you have prepared your Chromebook, open only one web browser (Safari, or Chrome or Firefox),
and go to sfhsmath.testportal.net. On the bottom of the page you will find something looking like this:
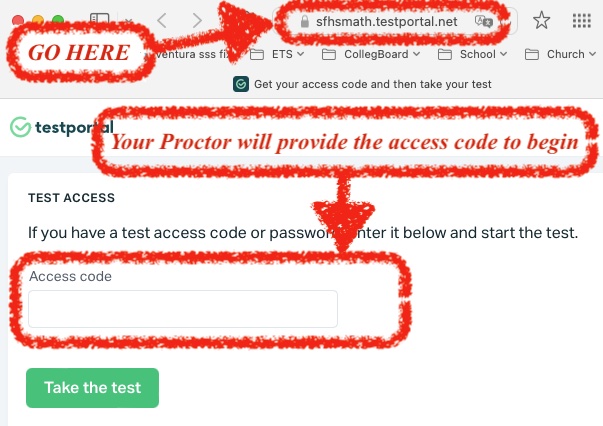
The proctor will provide an access code to type in the purple region at the bottom of the page. Before you start, activate "Do Not Disturb," turn off all notifications, alarms, and all other apps. Only have One tab on you web browser to take your exam.
It is a good idea to have a spare set of 4-AAA batteries (or a phone battery pack for color calculators) with you in case your calculator needs it during the test.
The exam is designed to cover Chapters R, 1, 2 and 3 of the Sullivan Algebra & Trigonometry Book,
though topics from Honors Algebra 1, and Honors Geometry may be needed to answer some questions. You may wish to go over your HAP Textbooks multiple choice questions at the end of chapters 1, 2, and 3. Some like to use the Khan Academy App.
The following are the key topics we have studied thus far:
sets, domain, synthetic division,
factoring difference of cubes, quadratic form of fractional exponents, abstract understanding of the completing the square technique,
absolute value, intercepts, linear inequality,
Quadratic inequality, negative exponents, line equation from points, functional notation, perpendicular slope, point-slope form of a line,
complex fractions, complex numbers, rationalizing denominators,
multiplying polynomials, variation, graphing lines, solving for x and y (substitution or simultaneous), midpoint formula, equations of circles, application of completing the square technique, variation word problems, and building functions to solve word problems.
Study Tips
It would be good to go over old quizzes and tests, review what you did well, and learn from any mistakes. Remember there are a lot of worksheets and practice tests at hw.mathorama.com, and Summer Prep for HAP. You may wish to use Khan Academy to review old topics. If you would like to practice multiple choice and free response questions that compine topics from different chapters, try old New York Regents Exams for Geometry, Algebra 1,
and the red boxed questions from Algebra 2.
The solutions and more exams can be found at NY Regents Tests
The exam is graded on a curve. Together with your third quarter exam, the Semeter 2 Exam represents 20% of your grade. You can compute your grade with the grade calculator at the bottom of the syllabus. In general, if your Sem 2 Exam is better that your Qtr 3 Exam, your grade will go up, and if it is worse, it will go down.
Finally, remember to go to bed at a descent hour and have a healthy breakfast in the morning so that you are rested enough to think clearly, and do your best. Good luck!
